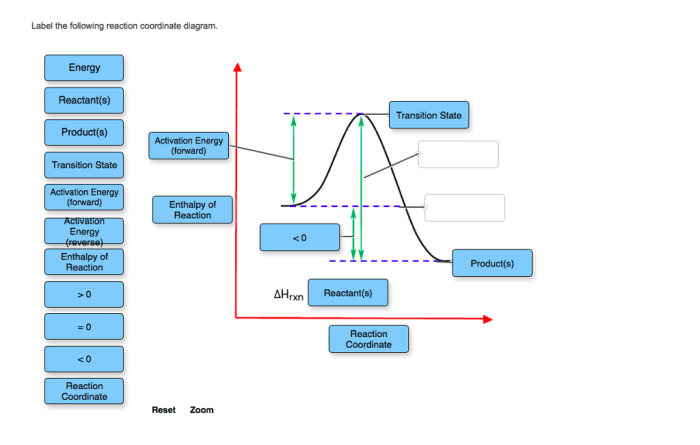
Label the following reaction coordinate diagram. – Labeling reaction coordinate diagrams is a crucial aspect of understanding chemical reactions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the concept, types, and applications of reaction coordinate diagrams, empowering readers to accurately interpret and utilize these powerful tools in their chemical studies.
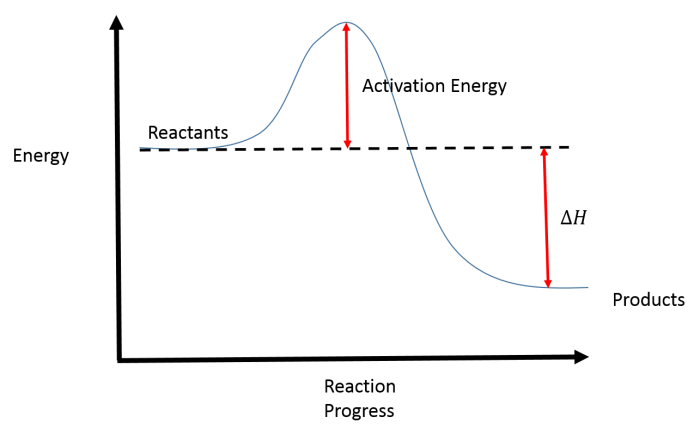
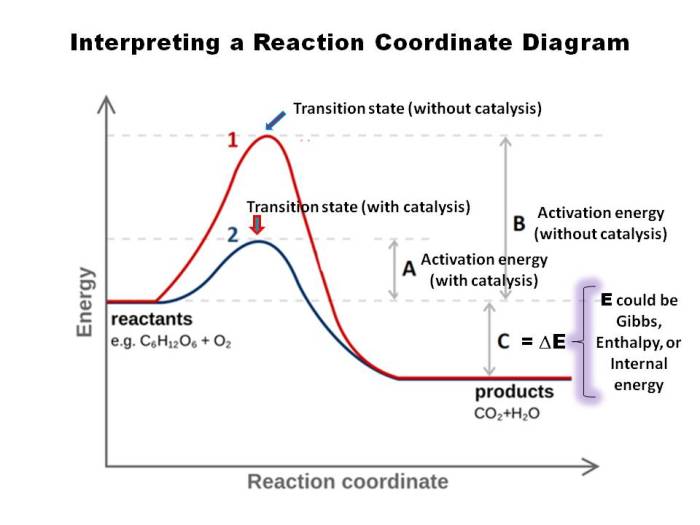
Reaction coordinate diagrams are graphical representations of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. They provide insights into the reaction pathway, transition states, and activation energies involved in the process. By understanding the key features and labeling conventions of reaction coordinate diagrams, chemists can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms and dynamics of chemical reactions.
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams: Label The Following Reaction Coordinate Diagram.
Reaction coordinate diagrams (RCDs) are graphical representations of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. They plot the energy of the system (E) against the reaction coordinate (s), which is a measure of the progress of the reaction.
RCDs can be used to visualize the energy changes that occur during a reaction, identify transition states, and determine the rate of the reaction.
Types of Reaction Coordinate Diagrams, Label the following reaction coordinate diagram.
There are two main types of RCDs:
- One-dimensional RCDsplot the energy of the system against a single reaction coordinate.
- Multi-dimensional RCDsplot the energy of the system against two or more reaction coordinates.
Labeling Reaction Coordinate Diagrams
The key features of an RCD are the:
- Reactants: The initial state of the system.
- Products: The final state of the system.
- Transition state: The highest energy point on the RCD.
- Activation energy: The energy difference between the reactants and the transition state.
- Reaction coordinate: A measure of the progress of the reaction.
To label an RCD, identify the reactants, products, transition state, and activation energy. Then, draw a line connecting the reactants and products, and label the line with the reaction coordinate.
Applications of Reaction Coordinate Diagrams
RCDs are used in chemistry to:
- Visualize the energy changes that occur during a reaction
- Identify transition states
- Determine the rate of a reaction
- Understand the mechanisms of chemical reactions
RCDs have been used to study a wide variety of chemical reactions, including:
- Gas-phase reactions
- Liquid-phase reactions
- Solid-state reactions
- Enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Advanced Topics in Reaction Coordinate Diagrams
RCDs are also used in computational chemistry to:
- Calculate the free energy surfaces of reactions
- Predict the rate of reactions
- Design new catalysts
RCDs are a powerful tool for understanding the mechanisms of chemical reactions. They can be used to visualize the energy changes that occur during a reaction, identify transition states, and determine the rate of the reaction.
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of a reaction coordinate diagram?
Reaction coordinate diagrams provide a visual representation of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction, allowing researchers to understand the reaction pathway and identify key features such as transition states and activation energies.
How do I label a reaction coordinate diagram?
Labeling a reaction coordinate diagram involves identifying the reactants, products, transition states, and activation energies, and accurately plotting them on the diagram according to their energy levels.
What are the different types of reaction coordinate diagrams?
There are various types of reaction coordinate diagrams, including one-dimensional diagrams that represent the energy changes along a single reaction coordinate, and multi-dimensional diagrams that depict the energy changes in a multi-dimensional reaction space.