Levels of ecological organization worksheet sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate tapestry of life, exploring the hierarchical structure of ecosystems and the dynamic interactions that shape their existence.
From the smallest building blocks of life to the vast expanses of biomes, this worksheet unravels the complexities of ecological organization, shedding light on the interconnectedness of all living organisms and their environment. Prepare to embark on an educational journey that will deepen your understanding of the natural world and its intricate workings.
Definition of Ecological Organization: Levels Of Ecological Organization Worksheet
Ecological organization refers to the hierarchical arrangement of living organisms within an ecosystem, from individuals to entire biomes. Understanding ecological organization is crucial for comprehending the intricate relationships and dynamics within ecosystems.
Each level of ecological organization has a specific definition:
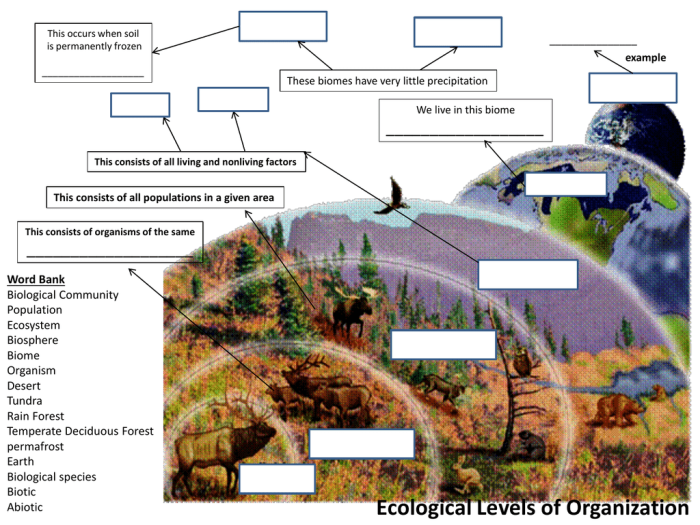
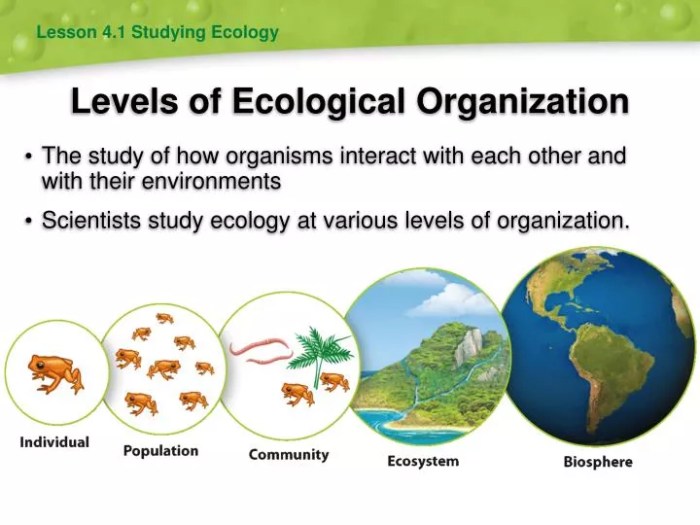
- Individual:A single living organism.
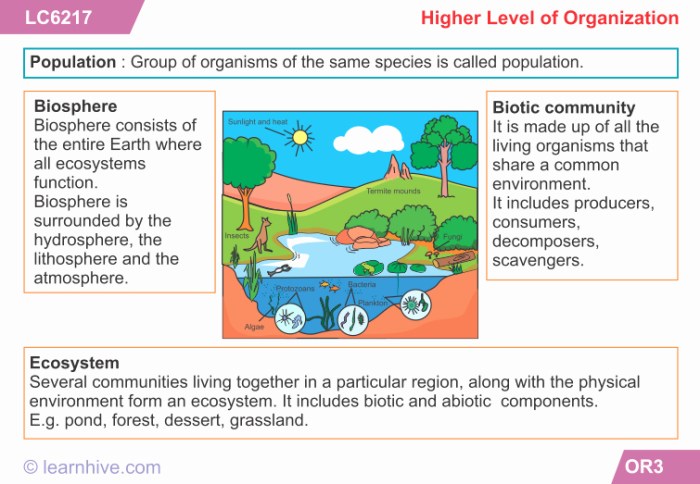
- Population:A group of individuals of the same species living in the same area.
- Community:All the populations of different species living and interacting in the same area.
- Ecosystem:A community of living organisms and their physical environment.
- Biome:A large-scale community of plants and animals that share similar climate and vegetation characteristics.
Hierarchy of Ecological Organization
| Level | Ukuran | Contoh |
|---|---|---|
| Individual | Single organism | Tree, fish, bird |
| Population | Group of same species | School of fish, flock of birds |
| Community | Different species in an area | Forest community, grassland community |
| Ecosystem | Community and physical environment | Pond ecosystem, forest ecosystem |
| Biome | Large-scale community with similar climate and vegetation | Tropical rainforest, temperate forest |
Interactions within and between Levels
Within and between levels of ecological organization, various interactions occur, including:
- Intraspecific interactions:Interactions within a population of the same species (e.g., competition, cooperation).
- Interspecific interactions:Interactions between populations of different species (e.g., predation, symbiosis).
- Trophic interactions:Interactions related to feeding and energy transfer (e.g., predator-prey relationships).
- Biotic-abiotic interactions:Interactions between living organisms and their non-living environment (e.g., plant growth affected by soil nutrients).
These interactions shape the structure and dynamics of ecosystems, influencing factors such as species distribution, abundance, and resource availability.
Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling
Energy flows through different levels of ecological organization, starting with producers (e.g., plants) that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to consumers (e.g., animals) through food chains and webs.
Similarly, nutrients cycle through ecosystems. Producers absorb nutrients from the environment, which are then passed on to consumers. Decomposers (e.g., bacteria) break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the environment for reuse.
These processes maintain the balance and productivity of ecosystems.
Stability and Resilience
Different levels of ecological organization contribute to the stability and resilience of ecosystems.
Diversity at lower levels (e.g., species diversity within a community) can increase ecosystem resilience, as it provides functional redundancy and reduces the impact of disturbances.
However, disturbances can disrupt ecosystem stability, affecting organisms at different levels. For example, a hurricane can impact individual trees (individual level) and alter the composition of the forest community (community level).
Human Impacts, Levels of ecological organization worksheet
Human activities can significantly impact different levels of ecological organization:
- Individual level:Hunting, overfishing, pollution
- Population level:Habitat destruction, invasive species
- Community level:Deforestation, urbanization
- Ecosystem level:Climate change, water pollution
- Biome level:Deforestation, desertification
These impacts can disrupt ecosystem structure, function, and stability, highlighting the importance of responsible human interactions with the environment.
FAQ Summary
What is ecological organization?
Ecological organization refers to the hierarchical structure of ecosystems, from individuals to biomes, and the interactions that occur within and between these levels.
How does energy flow through different levels of ecological organization?
Energy flows through ecosystems in a unidirectional manner, from producers to consumers and decomposers. At each level, some energy is lost as heat, resulting in a decrease in energy availability at higher levels.
How do human activities impact different levels of ecological organization?
Human activities can have significant impacts on ecosystems at all levels, from altering individual populations to modifying entire biomes. These impacts can include habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and the introduction of invasive species.